We have a strict honesty policy, but please note that when you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. Learn more.

In this Adobe Commerce (Magento) vs Shopify comparison, I take a deep dive into the key pros and cons of two widely-used ecommerce platforms. Which one is the better fit for your business needs?
The different versions of Adobe Commerce and Shopify
Before examining the differences between Adobe Commerce and Shopify in depth, it’s worth getting an understanding of the various flavors that both platforms come in. Let’s take a look at these now.
Adobe Commerce
There are three versions of Adobe Commerce to consider:
- Magento Open Source — free, open-source software that you install on your own server or hosting service.
- Adobe Commerce — a paid-for version of the service that, like Magento Open Source, you install and maintain on your own hosting setup, but one that comes with more features (for example advanced analytics, B2B features and AI tools).
- Adobe Commerce Cloud — a fully-managed, cloud-version of Adobe Commerce. It gives you access to all the key Adobe Commerce features, but with hosting and enhanced enterprise-level security features included.
These versions of the Adobe Commerce software are all made available at different price points.
Magento Open Source is free, but Adobe Commerce and Adobe Commerce Cloud involve negotiable pricing. This pricing isn’t made publicly available by Adobe, but our research indicates a pricing range of $22,000+ per year for access to Adobe Commerce, and $40,000+ per year for access to Adobe Commerce Cloud.
(It’s worth noting that Adobe Commerce Cloud’s pricing is based on Gross Merchandise Value — sales price of goods x number of goods sold — so pricing can vary enormously for this version of the software and, if you’re a successful merchant, end up being a lot higher than $40,000 per year.)
Shopify
There are basically two versions of Shopify available. First there’s its standard version, aimed at small businesses. This costs between $5 and $399 per month, depending on the plan you opt for (see my screenshot below).
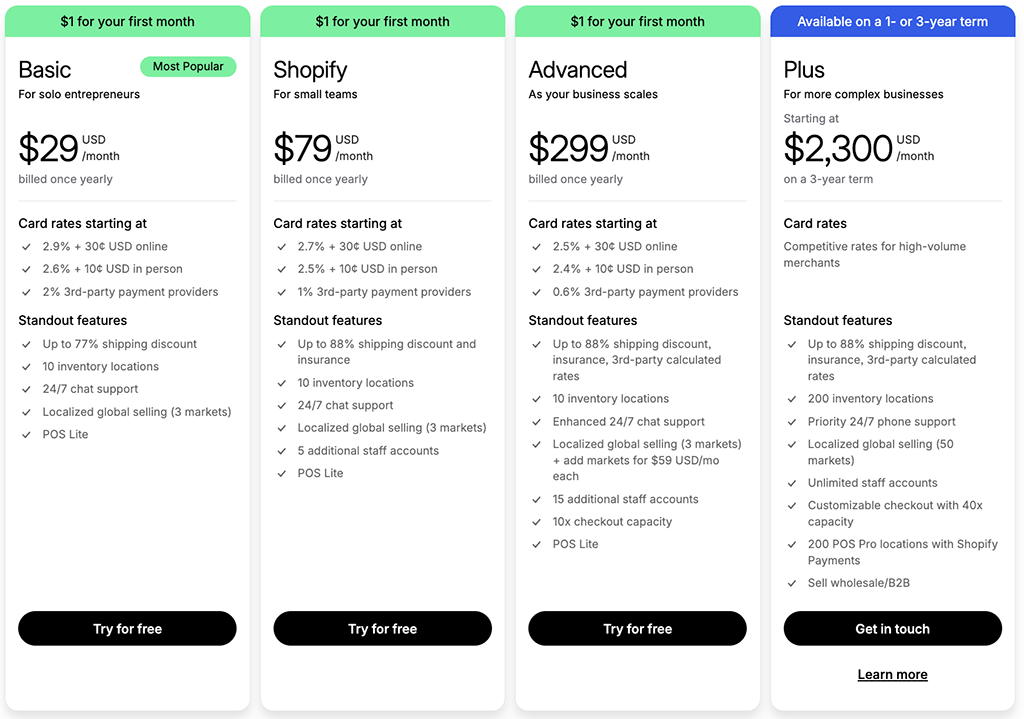
There’s also an enterprise version called Shopify Plus. Pricing for this is negotiable, but typically in the region of $2,300 per month.
Unlike Adobe Commerce, no version of Shopify involves open-source code, and all plans are ‘hosted’ — meaning that the software can only be run on Shopify’s servers.
As the core selling features of all three versions of Adobe Commerce are similar, in this comparison I’ll generally be using the phrase ‘Adobe Commerce’ to cover all three. However where necessary I’ll reference individual versions of the software.
I’ll start with a look at the key reasons to use Adobe Commerce over Shopify, before walking you through the areas where Shopify comes out on top.
Key reasons to use Adobe Commerce over Shopify
1. Adobe Commerce offers more flexibility
One of Adobe Commerce’s biggest selling points is the fact that it is based on open-source code — this allows merchants to customize nearly every aspect of their online store. From fully customized checkout processes to advanced product configurations, businesses have complete control over their ecommerce experience when using Adobe Commerce.
However, this level of flexibility comes at a cost — it requires significant technical expertise and ongoing development work, making it better suited for use by companies with dedicated IT teams.
Shopify, by contrast, operates within a highly controlled framework. While its enterprise offering, Shopify Plus, offers greater flexibility than standard Shopify plans, deep backend modifications remain limited.
That said, Shopify’s ‘Checkout Extensibility’ functionality — a recent addition to Shopify’s feature set — now allows Shopify Plus users to customize elements of the checkout process using approved extensions and APIs. But it still doesn’t provide the same level of control as Adobe Commerce.
Another key difference is how templates can be customized in both platforms. Shopify uses a proprietary templating language called ‘Liquid’, which allows merchants to edit themes, but using predefined rules. While Liquid is more accessible than raw coding, it imposes more constraints than Adobe Commerce’s fully customizable PHP framework.
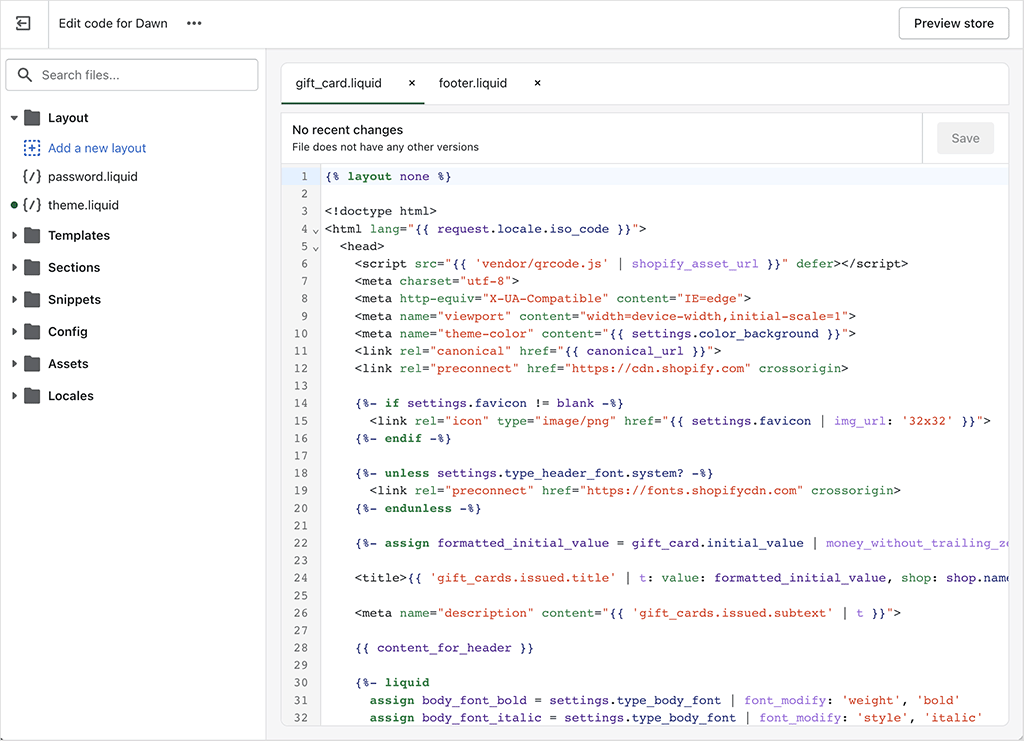
So while Shopify provides store owners with a nice balance between customization and simplicity, Adobe Commerce is the better option for businesses that require absolute creative and functional freedom.
2. Adobe Commerce scales better for very large businesses
Adobe Commerce is built for high-traffic, high-volume ecommerce operations (making it the platform of choice for major brands like Nike, Ford and HP).
Unlike Shopify, which operates within a managed infrastructure, Adobe Commerce allows businesses to fully control their hosting environment and optimize performance for complex catalogs and global operations.
This flexibility is particularly beneficial to enterprise businesses with custom infrastructure needs, such as those requiring advanced database management or highly-tailored server configurations.
That said, Shopify has made significant strides in scalability over the years. Its multi-server architecture and global CDN ensure reliable performance, even during extreme traffic surges. Shopify stores have demonstrated excellent stability on high-demand events like Black Friday, making traffic handling a non-issue for most businesses.
However, Shopify Plus still imposes restrictions on database control, checkout customization and server optimizations — key factors for enterprises with specialized infrastructure needs. And Shopify’s API rate limits can potentially slow bulk product updates.
3. Adobe Commerce handles multi-store management better
Adobe Commerce is one of the best platforms for managing multiple online stores under different brands, regions or pricing structures.
With its multi-store functionality, businesses can run multiple storefronts — each with its own domain, currency, language and product catalog — all from a single backend. This makes it a powerful solution for companies that need centralized control over multiple stores while maintaining regional or brand-specific variations.
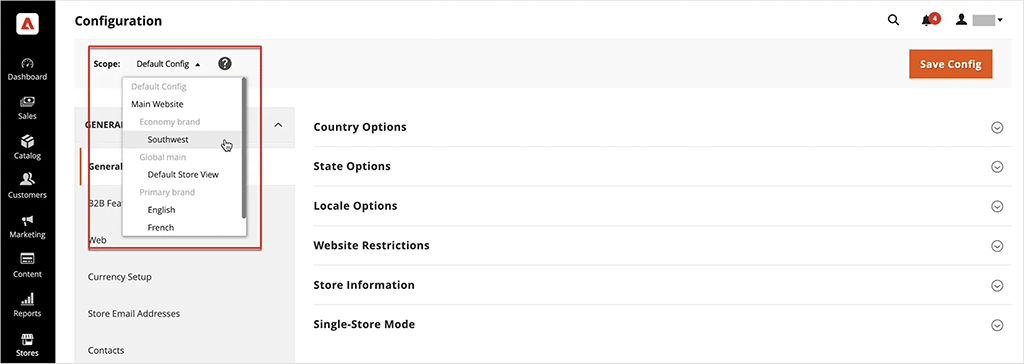
Standard Shopify plans are by contrast limited to a single store per account. This means that operating multiple stores on the non-enterprise version of Shopify involves creating and managing multiple Shopify accounts — and logging into individual admin dashboards to change settings and manage subscriptions.
(Shopify merchants can use third-party apps like Syncio or Multi-Store Sync Power to synchronize inventory, products and orders across their stores, but these solutions can add costs and complexity.)
Shopify Plus is better here: it lets you manage up to nine expansion stores in addition to your primary store. But even so, each expansion store functions independently, requiring its own setup and management, similar to standard accounts.
Ultimately if you need a simple, single-store solution, Shopify works well, but for those running multiple distinct brands or lots of regional storefronts, Adobe Commerce arguably provides a more efficient and scalable approach.
4. Adobe Commerce offers greater payment processing flexibility
Adobe Commerce gives merchants more control over payment processing than Shopify, supporting around 370 third-party payment gateways without imposing any additional transaction fees (i.e., users only pay the standard fees charged by their chosen payment provider). This makes it an attractive option for businesses that process a high volume of transactions or need access to specific regional payment providers.

Shopify, by contrast, supports about 100 third-party payment gateways and charges transaction fees of 0.6% to 2% (depending on plan) if you use one of them.
The only way to avoid transaction fees with Shopify is by using its built-in payment gateway, ‘Shopify Payments’ — but this is only available in 23 countries.
While Shopify Payments simplifies processing and eliminates extra costs, merchants outside of supported regions (or those who want to use alternative payment processors) may find these fees unwelcome.
Ultimately, for businesses that need maximum payment flexibility, Adobe Commerce’s larger selection of gateways and its lack of transaction fees give it a significant edge over Shopify.
5. Adobe Commerce allows full checkout customization
Unlike Shopify, Adobe Commerce provides merchants with complete control over the checkout experience, making it the stronger choice for businesses that require custom payment flows, advanced verification steps, or highly specific checkout modifications.
The platform lets you freely adjust your checkout layout, add custom fields, modify payment logic or integrate third-party services into the selling process.
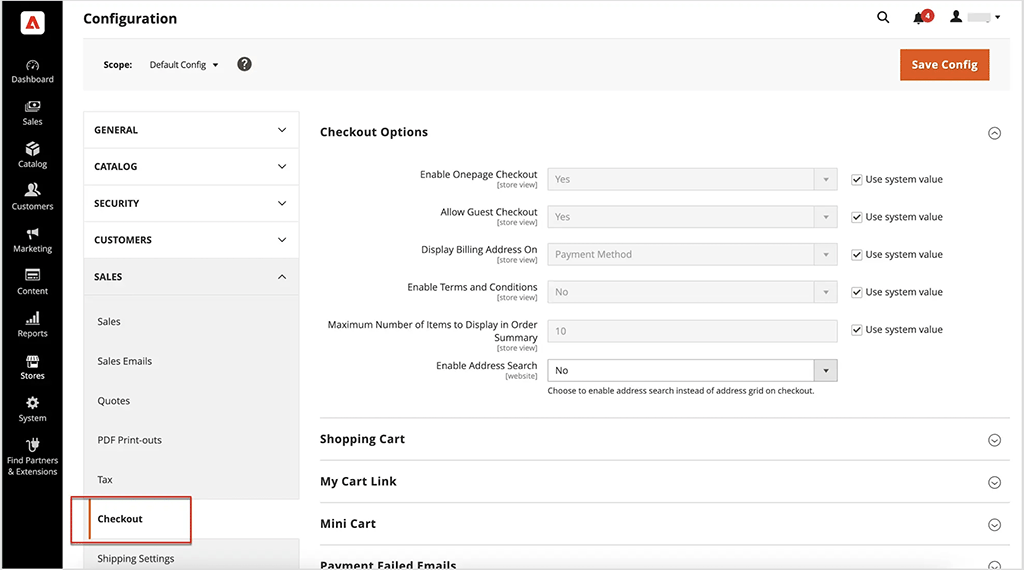
On standard Shopify plans, checkout customization is much more limited. Merchants can personalize the checkout page with basic branding options, such as adding a logo, adjusting colors and modifying typography. However, direct layout modifications, custom checkout fields and payment flow changes are not permitted.
Shopify Plus offers more flexibility here with its ‘Checkout Extensibility’ framework: this allows more significant checkout modifications using Shopify-approved apps and APIs. But while this facilitates the addition of custom elements like additional fields, upsell offers and localized checkout flows, it still doesn’t let merchants directly modify a checkout’s code or layout.
Now despite these limitations, I should mention that Shopify’s checkout is widely regarded as one of the most optimized in the industry. It features a one-page checkout designed for speed and simplicity and its infrastructure is capable of handling up to 40,000 checkouts per minute — a level of scalability well-suited for businesses experiencing high-volume traffic.
(So arguably, modifying a Shopify checkout extensively is not always necessarily the best thing to do in any event.)
However for businesses that need full control over their checkout process, Adobe Commerce is unquestionably the more flexible option.
6. Adobe Commerce provides more control over SEO
Adobe Commerce gives merchants full control over their site’s SEO, making it a better choice for businesses that need to make deep technical SEO optimizations.
Adobe Commerce merchants can customize URL structures, creating clean, search-friendly links without being forced into using predefined subdirectories. Shopify by contrast enforces a more rigid URL structure, requiring merchants to use ‘/collections/’ and ‘/products/’ in their URLs — this may limit certain SEO strategies a bit.
Adobe Commerce also allows for unrestricted metadata editing, enabling businesses to modify titles, descriptions and alt text at the product and category level. Shopify offers basic metadata control but caps title tags at 70 characters, which can lead to truncation in search results and potentially lower click-through rates.
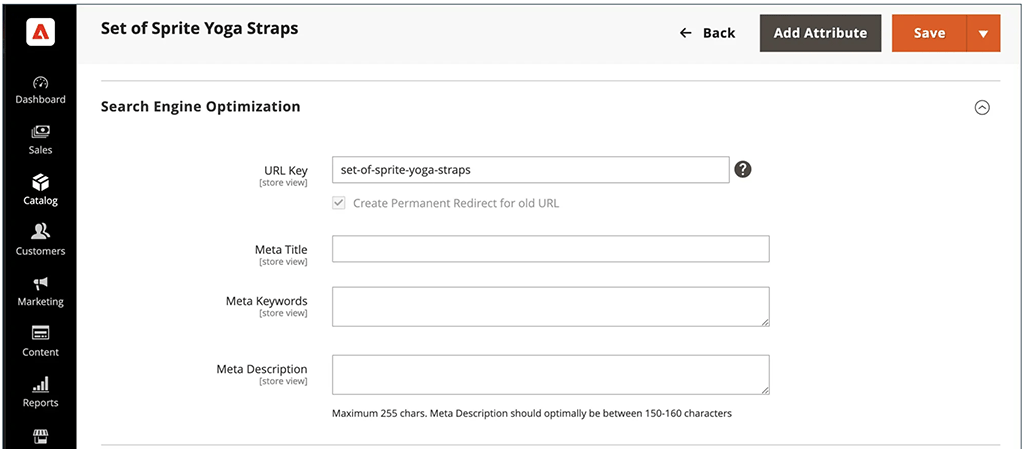
Another advantage of Adobe Commerce is its inclusion of a Schema markup editor (Schema is data that lets search engines know more about your products and content). Shopify doesn’t provide a similar feature, meaning that merchants will need to rely on third-party apps (or coding) to modify Schema markup.
Additionally, Adobe Commerce offers full control over canonical tags and redirects, allowing businesses to manage duplicate content and URL changes with precision. Shopify includes automatic canonicalization and built-in 301 redirect tools, but these don’t offer quite the same level of control over these SEO elements.
And finally, Adobe Commerce gives you more control over technical SEO — much like WordPress, it gives merchants full control over hosting, speed optimizations and page structure. Shopify, by contrast, provides a simpler, pre-configured SEO setup that is more user-friendly but less adaptable.
7. Adobe Commerce gives you full control over hosting and performance optimization
Because Adobe Commerce can operate as a self-hosted platform, it allows businesses to choose their own hosting provider, configure caching solutions and optimize server performance based on their precise needs.
Adobe Commerce merchants can fine-tune server response times, implement advanced caching strategies and scale their infrastructure, ensuring optimal speed and reliability. This flexibility is ideal for high-traffic businesses or those requiring custom server setups.
Shopify, by contrast, provides fully managed hosting, eliminating the need for server maintenance but also restricting choices around performance optimizations. While Shopify’s infrastructure is built for reliability, and automatically scales during traffic spikes, merchants cannot adjust server configurations, implement custom caching strategies, or fine-tune backend performance.

Adobe Commerce also allows businesses to configure their own ‘content delivery network’ (CDN), improving global site speed, while Shopify uses a built-in CDN that provides no merchant-level control.
Additionally, server-side optimizations, such as database tuning and PHP version selection, are entirely customizable in Adobe Commerce, but again, Shopify manages these internally.
While Shopify’s managed infrastructure offers a simpler, hands-off hosting solution, businesses needing absolute control over hosting and performance may find Adobe Commerce the better option.
(As I mentioned earlier, this level of control can also be useful when it comes to improving technical SEO.)
8. Adobe Commerce offers superior flexibility for managing large, complex product catalogs
Adobe Commerce is built to handle huge product catalogs, making it a strong choice for businesses managing hundreds of thousands of SKUs.
It lets merchants create highly customized product listings with unlimited variants and options, and allows for detailed product configurations across multiple attributes.
This level of flexibility is particularly beneficial for online businesses selling things like fashion, furniture, or industrial equipment, where customers may wish to customize products extensively.
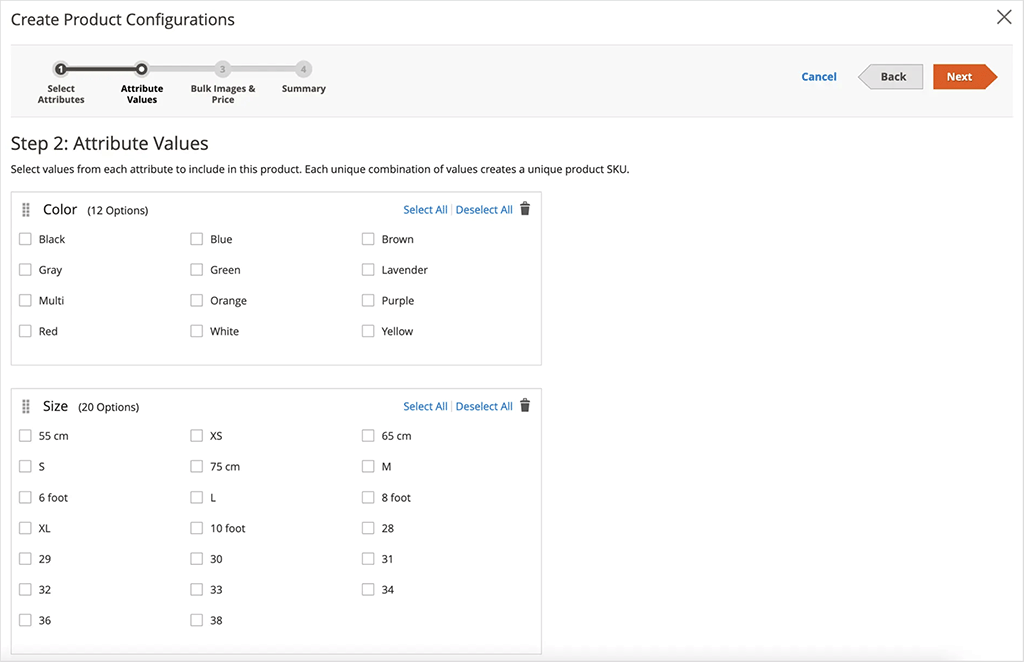
Shopify, by contrast, limits each product to 3 options (e.g, size, color or material) and 100 variants (combinations of these). This can be restrictive for businesses selling items that comes in lots of different shapes and sizes.
There is a workaround available here, however: Shopify merchants can install third-party apps like Infinite Options to bypass these product option limitations. This can add extra costs and complexity to catalog management, though.
Another constraint in Shopify is its variant upload limit. Stores with 50,000 or more variants are subject to a daily cap of 1,000 new variants (Shopify Plus merchants are exempt from this restriction, however).
Happily, Adobe Commerce doesn’t impose variant or bulk upload limits at all — giving merchants full control over their inventory updates and scalability.
So for businesses with complex product configurations and large inventories, Adobe Commerce offers a significantly more flexible and scalable solution.
9. Adobe Commerce provides greater control over automation and workflows
Adobe Commerce offers more flexibility when it comes to ecommerce automation.
As an open-source platform, it allows for custom scripting, advanced API integrations and tailored automation workflows, enabling businesses to fine-tune processes like inventory synchronization, pricing adjustments and multi-supplier coordination.
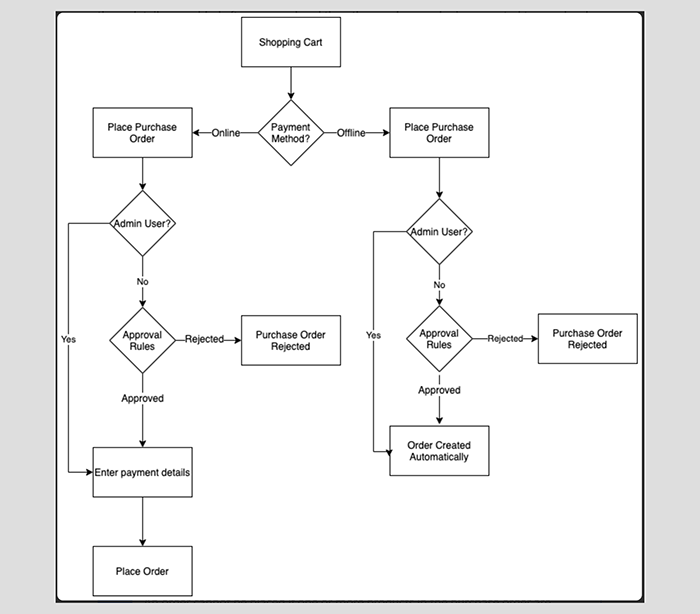
Shopify provides automation through its ‘Shopify Flow’ system, which is now available on most of its plans. Flow enables merchants to create rule-based triggers for common tasks, such as sending low-stock alerts, tagging high-value customers, or automating order routing.
However, more advanced automation, involving full API access and endpoints, is only available on higher-tier Shopify plans.
(Additionally, Shopify’s API rate limits, while fairly generous, can restrict the number of automated processes performed in a short period — for example those involving bulk product updates or high-volume data syncing.)
10. Adobe Commerce offers greater control for businesses in regulated industries
Businesses working in certain industries — such as pharmaceuticals, financial services and government procurement — must adhere to strict compliance regulations involving data security, reporting and payment processing.
And Adobe Commerce, being fully open-source, allows businesses to customize their compliance protocols to meet these requirements. This flexibility makes it an attractive choice for organizations that need complete control over how customer data is stored, processed and secured.
For example, Adobe Commerce merchants can choose their hosting provider to ensure GDPR-compliant data storage in the EU; implement custom encryption and authentication measures; and modify checkout and payment processes to meet financial or industry-specific regulations. These capabilities are particularly valuable for companies handling sensitive customer data, high-value transactions, or government contracts.

But Shopify, as a ‘Software as a Service’ company, controls the infrastructure used by merchants, meaning that they have to operate within Shopify’s built-in security framework.
While Shopify is PCI DSS Level 1 certified and provides strong security protections — including SSL encryption, fraud analysis and automatic compliance updates — it doesn’t allow merchants to modify security and data protection settings at a deep level.
For businesses with standard ecommerce compliance needs, this situation is usually fine, but for those operating under stringent regulatory requirements, Adobe Commerce may be the better choice.
So those are my thoughts on the advantages of using Adobe Commerce over Shopify — if you want to try out the platform you can do so here.
Now I’m going to explore the reasons why you might want to use Shopify.
Key reasons to use Shopify over Adobe Commerce
1. Shopify is significantly easier to use and faster to set up
Starting an online store can be daunting for non-technical entrepreneurs, but Shopify streamlines the process with its intuitive drag-and-drop interface and its large range of pre-designed, easy-to-edit templates.
This streamlined setup enables you to launch your store in as little as a few hours and without having to write any code whatsoever.
By contrast, an Adobe Commerce setup typically requires configuring servers, managing databases and performing theme modifications via coding. This leads to a much more technical process and a steeper learning curve.
As a result, launching an Adobe Commerce store can take weeks or even months, significantly delaying your time-to-market.
(For the record, Adobe Commerce states that most stores take around six months to be fully deployed. Shopify claims that even enterprise-level stores using the ‘Shopify Plus’ version of the platform can be launched in under 90 days — half the time of an Adobe Commerce go-live.)
Furthermore, Shopify’s intuitive content management system ensures that day-to-day tasks, like adding products or managing inventory, are all extremely straightforward to perform. Adobe Commerce’s steep learning curve can make these routine tasks much more time-consuming, potentially diverting focus from other critical business activities.
Ultimately, Shopify’s user-friendliness represents one of the biggest reasons to use it over Adobe Commerce.
2. Shopify handles hosting for you
Managing the technical infrastructure of an online store can end up being a significant burden for small to medium-sized businesses.
Shopify alleviates this challenge by providing a fully hosted solution, meaning that web hosting, security and software updates are all managed for you by the company.
This approach ensures your store remains fast, secure and up-to-date without any extra effort on your part; and a guaranteed 99.99% server uptime means your store stays fully accessible to customers around the clock.

By contrast, Adobe Commerce is a self-hosted platform: this gives you more control over your hosting environment but shifts all related responsibilities over to you.
So using Adobe Commerce means selecting your own hosting provider — with good ones often being very expensive — and handling critical tasks like installing security patches and performing software updates yourself. Without diligent management, these responsibilities can potentially expose your store to significant security vulnerabilities and performance issues.
Of the two platforms, the one that most reduces risk and ongoing maintenance costs for businesses is definitely Shopify.
3. Shopify is usually a lot cheaper
Shopify provides a transparent, fixed-cost pricing model, making it easier for businesses to budget.
Its core plans are priced as as follows:
- $29 per month for the ‘Basic’ plan
- $79 per month for the ‘Shopify’ plan
- $299 per month for the ‘Advanced’ plan.
Each of these plans includes themes, hosting, security, and a comprehensive suite of ecommerce features.
For those just starting out, Shopify also offers a $5 per month ‘Starter’ plan; this provides a straightforward way to integrate ecommerce into your existing website or social channels.

You can explore the key features of all Shopify plans through its free trial.
👉Trial details: Shopify free trial (extendable to 3 months)
The most basic version of Adobe Commerce — ‘Magento Open Source’ — is free to download, but the associated costs can add up quickly. Expenses such as hosting fees and development costs for setup and ongoing maintenance must also be factored into your budget.
And using the paid-for versions of Adobe Commerce can be extremely expensive. Pricing is negotiable, but my research suggests a pricing range of at least $22,000 per year for access to Adobe Commerce, and a minimum of $40,000+ per year for access to Adobe Commerce Cloud.
And as I mentioned earlier, Adobe Commerce Cloud’s pricing is based on Gross Merchandise Value — sales price of goods x number of goods sold. This means that if you’re a high-volume seller, the fees for Adobe Commerce Cloud can really mount up.
In fact, a recent study shows that Shopify’s total cost of ownership (TCO) — which considers both the upfront expenses and the ongoing costs of maintaining and operating a platform — is approximately 29% lower than Adobe Commerce’s.

👉 You can get a full breakdown of Shopify costs and fees in our in-depth Shopify pricing guide.
4. Shopify provides more apps and integrations than Adobe Commerce
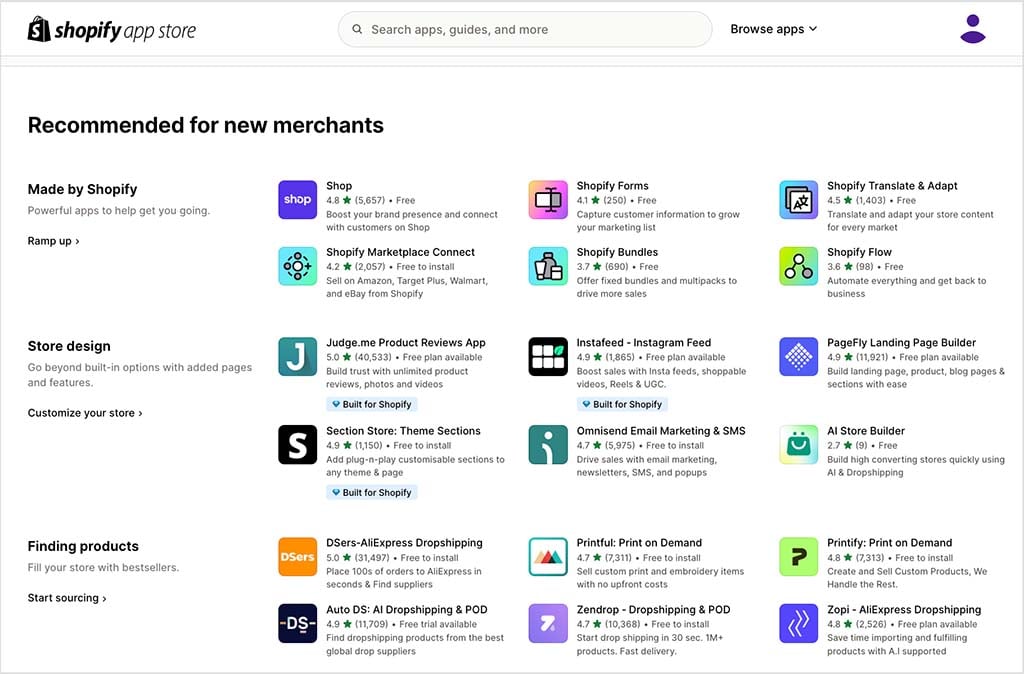
Expanding your online store’s capabilities is often essential for growth, and Shopify offers a significant advantage here in the form of its well-stocked app store. This contains a selection of over 16,000 apps which cover everything from marketing automation and inventory management to customer support, analytics and AI-driven personalization.
(Significantly, these are all vetted from a security and compatibility point of view by Shopify before they are added to the Shopify app store.)
Designed for ease of use, most Shopify apps can be installed in just a few clicks — and using them typically requires little to no technical expertise. Whether you’re looking to launch a loyalty program, streamline fulfillment, or integrate with social media and marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, Shopify’s App Store offers an accessible, plug-and-play solution.
By contrast, Adobe Commerce’s extensions marketplace features around 4,000 extensions, giving Shopify a 4-to-1 advantage in terms of app availability.
And although Adobe Commerce’s extensions provide deep customization opportunities, many require manual installation, developer intervention and additional configurations. This complexity can make expanding store functionality more time-consuming and costly than doing so with Shopify, especially for non-technical merchants (who may have to resort to developer support to use certain apps).
So for businesses seeking a streamlined, user-friendly way to enhance their store’s functionality, thanks to its app store, Shopify wins.
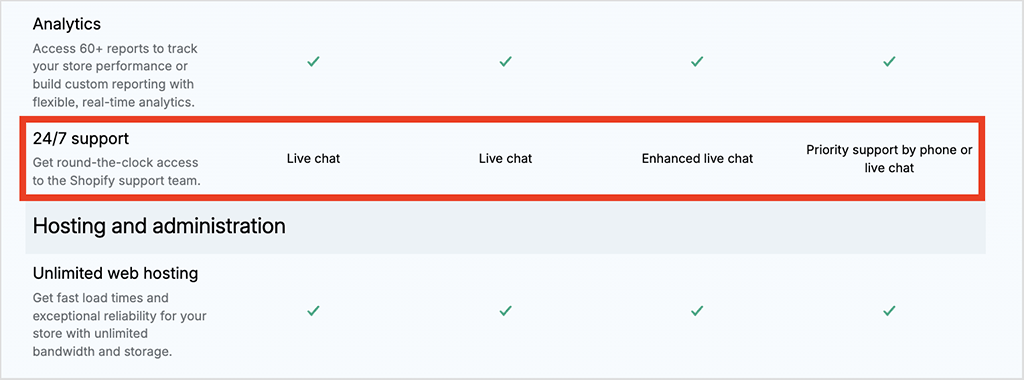
5. Shopify offers 24/7 support on all plans
Shopify provides round-the-clock customer support via live chat on all plans (with phone support available on its enterprise ‘Shopify Plus’ offering too).
With Adobe Commerce however, accessing customer support is not so straightforward.
If you’re using the entirely free version of Adobe Commerce — Magento Open Source — there is no official customer support, meaning users must rely on community forums, documentation and third-party developers for troubleshooting.
For those using the paid versions of Adobe Commerce, official support is included, however. Even then, response times and service levels depend on specific support packages.
Ultimately for businesses that want instant, reliable help without extra costs, Shopify’s 24/7 support structure — particularly its always-available chat and email assistance — gives it a clear edge over Adobe Commerce.
6. Shopify provides built-in security and PCI compliance
Security is a top priority in ecommerce, as a single data breach can result in financial losses and damage customer trust.
Helpfully, Shopify simplifies security by offering built-in protection across all stores, ensuring merchants don’t have to manage it themselves.
All Shopify stores are PCI DSS Level 1 compliant, meaning they meet the highest standards for securely processing credit card transactions.
(PCI — Payment Card Industry — compliance is a set of security standards required for businesses that handle credit card payments; these are designed to protect sensitive customer data from fraud and breaches.)
Shopify also provides free SSL certificates for every store, encrypting customer data and keeping transactions secure. Additionally, its fraud detection tools help merchants identify and prevent suspicious transactions, reducing chargebacks and protecting revenue.
But if you’re using a self-hosted version of Adobe Commerce, ensuring site security rests entirely with the individual store owner. Merchants must manually install SSL certificates, maintain PCI compliance and apply security patches to keep their store protected. Failure to do so can leave an Adobe Commerce store vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches and compliance violations.
And for businesses without dedicated security expertise, this ‘self-managed’ security setup can be complex, time-consuming or expensive to sort out.
7. Shopify evolves continuously and rolls out new features automatically
One of the key benefits of Shopify is that it continuously evolves, rolling out new features, integrations and performance updates automatically. Store owners don’t need to worry about manually upgrading their software — everything happens seamlessly in the background, ensuring merchants always have access to the latest tools.
For example, in the most recent round of ‘Shopify Editions’ upgrades, over 150 updates were introduced across various areas, including AI-powered automation, expanded sales channels and backend improvements.
Adobe Commerce, by contrast, follows a traditional software update model. While the platform regularly releases improved features, the updates necessary to access them must be manually performed (even if you’re using the ‘Adobe Commerce Cloud’ version of the platform).
This often requires developer assistance, leading (once again!) to additional costs. And as I discussed earlier, failing to keep Adobe Commerce updated can result in compatibility issues with extensions and potential security vulnerabilities.
8. Shopify provides powerful built-in point-of-sale features
A point-of-sale (POS) system lets merchants sell in physical locations (retail stores, marketplaces etc.) while keeping inventory synced with their online store.
Shopify includes a built-in POS system on all its plans, even its $5 per month ‘Starter’ one. This lets merchants process sales using a wide range of hardware including smartphones, tablets, card readers, barcode scanners, and tills — with everything managed from a single Shopify dashboard.
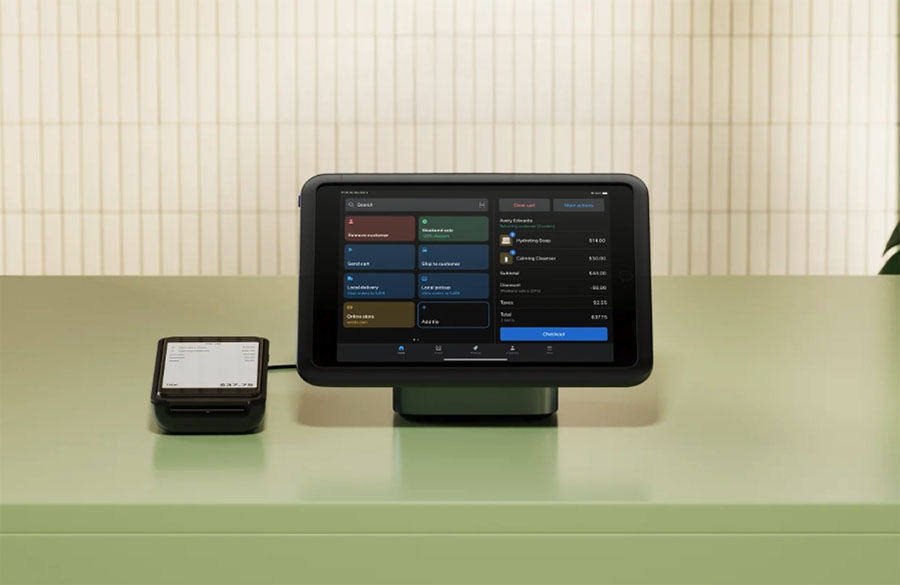

The bundled Shopify ‘POS Lite’ version of system facilitates basic transactions, while Shopify ‘POS Pro’ ($89/month per location) unlocks advanced features, including:
- buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS)
- local delivery
- exchanges and in-store returns
- custom printed receipts
- purchase order creation
- automatic discounts applied at checkout
- low stock warnings.
(Shopify Plus users can use ‘POS Pro’ in up to 20 location as part of their subscription.)
By contrast, Adobe Commerce does not offer a built-in POS system — instead, merchants must rely on one of 69+ third-party extensions (e.g., Square, PayPal, Zettle etc.).
While this provides flexibility for businesses with existing POS setups, it adds extra costs, more setup time and potential compatibility issues.
💡 Tip: You can learn more about Shopify POS in our Shopify POS pricing guide.
9. Shopify makes dropshipping and print-on-demand easier than Adobe Commerce
If you’re aiming to start a dropshipping or print-on-demand (POD) business, Shopify is by far the better choice of the two platforms. It gives you access to over 635 dropshipping apps and more than 580 print-on-demand ones — a large selection of tools with which to try the dropshipping or POD model out.
These apps allow merchants to display a huge range of products on their stores that can be manufactured or fulfilled automatically by third-party companies (AliExpress, Spocket, Zendrop, Modalyst, Printful, Printify etc.)
By contrast, Adobe Commerce only integrates with a few dropshipping and print-on-demand platforms (and significantly, these don’t include big hitters AliExpress or Printify). Furthermore, setting up these integrations requires considerable technical effort — you will have spend time manually configuring supplier relationships, and troubleshooting inventory syncing issues.
Ultimately, if you’re looking for a quick, hassle-free entry into dropshipping or print-on-demand, Shopify is the clear winner.
10. Shopify makes it easier to sell on other platforms
Shopify makes it incredibly easy to expand beyond your own ecommerce store and sell on other platforms — for example, Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Facebook, Instagram, TikTok and Google Shopping.
In short, it lets you sell products on multiple marketplaces and platforms easily from a single dashboard, using native integrations.
Adobe Commerce, on the other hand, doesn’t include built-in marketplace integrations. To sell on channels like Amazon or eBay, you’ll need to install third-party extensions like ‘M2E Pro’ or ‘Webkul Multi-Channel Connector’.
While these extensions offer more customization options, they require additional configuration and maintenance, making the process far more cumbersome than Shopify’s approach.
So if your goal is to maximize exposure (and revenue) by selling across multiple sales channels, Shopify is usually the better choice.

11. It’s easier to sell internationally with Shopify
Expanding into international markets can be complicated, but Shopify simplifies global selling with built-in multi-currency, localization and regional pricing tools. Its ‘Markets’ feature, an all-in-one cross-border commerce solution, allows merchants to:
- automatically display prices in local currencies, with real-time exchange rate updates
- offer region-specific pricing and tax settings without using multiple storefronts
- translate stores into 20 languages.
Adobe Commerce, by contrast, requires significantly more manual effort to achieve similar results.
While it supports multi-currency transactions, merchants must manually configure exchange rates or integrate their store with a third-party service to keep them updated.
For multilingual support, Adobe Commerce provides a localization framework, but translations are not automatic. Merchants must manually input translated content for each store view or rely on third-party extensions to automate translations.
By contrast, Shopify’s bundled translation features allow merchants to quickly and automatically translate content across their storefronts. (Its ‘Translate and Adapt facilitates two automatic translations; paid-for apps can be used if you need more.)
Additionally, Adobe Commerce’s approach to international selling is based on multi-store functionality, which requires merchants to create separate storefronts for different countries, each with its own pricing, tax rules and content.
With Shopify, you just operate one store, which is automatically shown in the relevant language / currency based on a user’s location.
Adobe Commerce vs Shopify: the verdict
Both Adobe Commerce and Shopify are powerful ecommerce platforms, but they cater to rather different types of businesses and users — and ultimately, making the decision between them is going to boil down to your technical expertise, budget and business needs.
If you’re running a large enterprise with complex requirements — think multi-store management, advanced backend automation, or extremely bespoke checkout experiences — Adobe Commerce offers a level of flexibility that Shopify can’t quite match. Its open-source heritage gives you full control over hosting, development and security, making it a strong option for businesses that need tailored solutions.
But that flexibility comes with higher development costs, ongoing maintenance and a much steeper technical learning curve.
So for many businesses, Shopify is going to be the much more practical choice. It’s significantly easier to use, and provides a quick setup process that can lead to a store going live in days rather than (as is often the case with Adobe Commerce projects) weeks or months.
Shopify also simplifies international selling with built-in multilingual and multi-currency tools — merchants can translate their store into up to 20 languages and set region-specific pricing effortlessly. While Adobe Commerce supports global expansion, achieving the same level of localization often requires third-party extensions and a significantly more manual setup.
Finally, Shopify’s large app ecosystem (containing over 16,000 apps) makes it easy to extend your store’s functionality without needing a developer.
Ultimately, if you’re a large-scale enterprise with highly specific needs, a big budget and a development team, Adobe Commerce offers a huge amount of flexibility. Most other types of ecommerce businesses — and especially those involving dropshipping or print on demand — will usually be better off with Shopify.
You’ll find links to the Adobe Commerce download and the Shopify free trial below.
If you have any queries or thoughts of your own on either tool, do leave them in the comments.
Key alternatives to Adobe Commerce and Shopify
While Adobe Commerce and Shopify are two of the most popular ecommerce platforms, there are plenty of alternatives available (you’ll find detailed information about many of these in our Shopify alternatives guide).
For a self-hosted, open-source option, WooCommerce — a WordPress plugin — is a solid choice. It offers lots of flexibility but, like Adobe Commerce, requires you to deal with your own hosting, security and software updates. You can learn more about this platform in our WooCommerce vs Shopify and WooCommerce vs BigCommerce comparisons.
BigCommerce is a good hosted alternative to Adobe Commerce and Shopify. Like Adobe Commerce, BigCommerce comes with excellent multi-storefront functionality, and it also competes well with Shopify in terms of general ecommerce features. Check out our BigCommerce review and our BigCommerce vs Shopify comparison to learn more about this platform.
For businesses prioritizing POS features, Square is also worth a look. It’s especially good for retailers and food service businesses needing seamless online and in-person sales. Check out our Square vs Shopify shootout for more details on this solution.
If you need a WordPress-compatible ecommerce plugin, Ecwid is a great option. Unlike WooCommerce, it’s not open-source — and accordingly offers better customer support and an easier setup. Check out our comprehensive Ecwid review and our Ecwid vs Shopify comparison to see if it’s a good fit for you.
Lastly, if you’re looking for a general website builder that includes ecommerce, Wix and Squarespace are also well worth a look.
Both offer intuitive design tools and built-in selling features, making them ideal for small businesses, creatives and solopreneurs. While they don’t match Shopify or Adobe Commerce in scalability, they provide a versatile, user-friendly approach to website creation and online selling. Our in-depth Wix review, Squarespace review and Wix vs Shopify vs Squarespace comparison cover them in more detail.
No comments